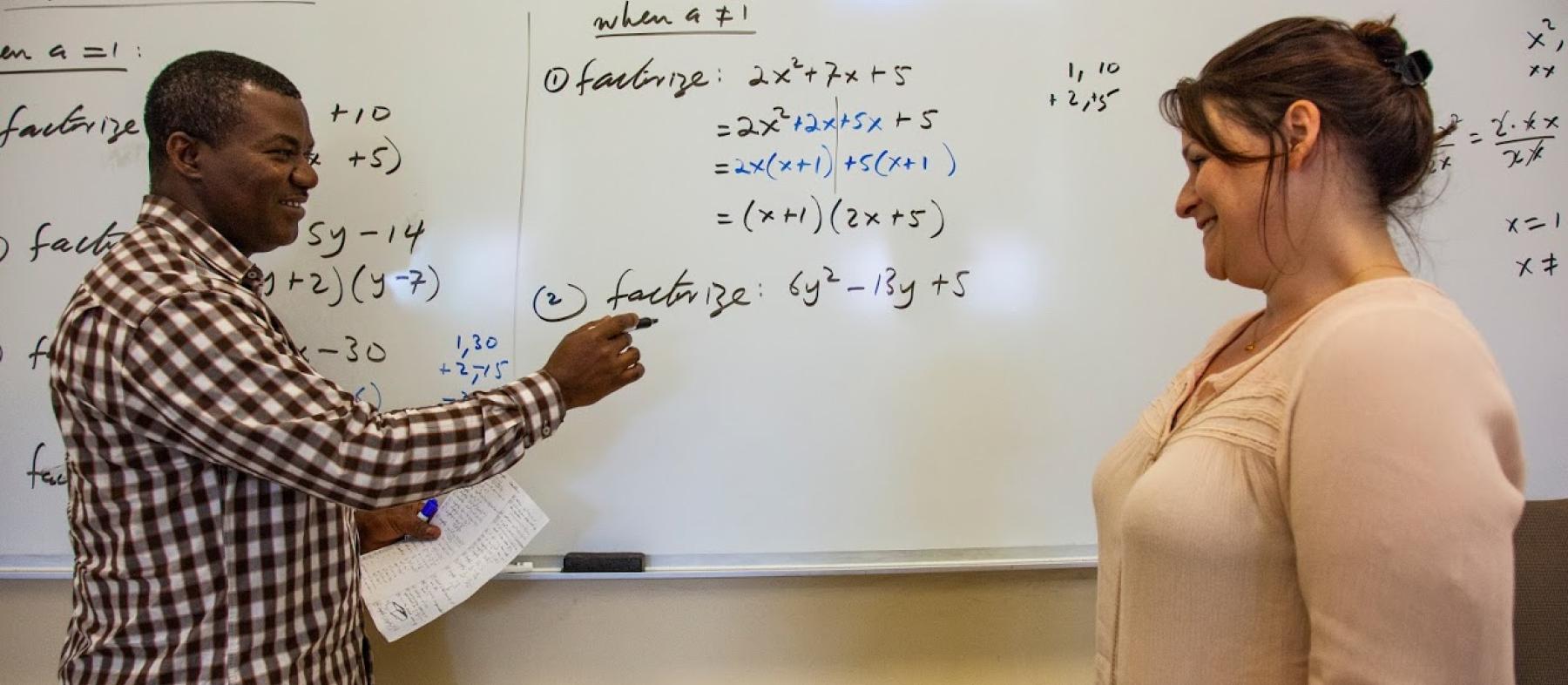MAT 231 Applied Calculus MAT 231 Sample Syllabus Prerequisite : MAT 123 or appropriate placement scoreCredits : 3This course is designed for students considering a major in business, pharmaceutical, social, and life sciences.
MAT 233 Calculus I MAT 233 Sample Syllabus Prerequisite : MAT 124Credits : 4
MAT 234 Calculus II MAT 234 Sample Syllabus Prerequisite : MAT 233Credits : 4
MAT 235 Calculus III MAT 235 Sample Syllabus Prerequisite : MAT 234Credits : 4
MAT 237 Probability & Statistics for Engineers and Scientists MAT 237 Sample Syllabus Prerequisite : MAT 234Credits : 3
MAT 238 Differential Equations MAT 238 Sample Syllabus Prerequisite : MAT 235Credits : 3
MAT 243 Linear Algebra MAT 243 Sample Syllabus Corequisite : MAT 238Credits : 3
Back to Top